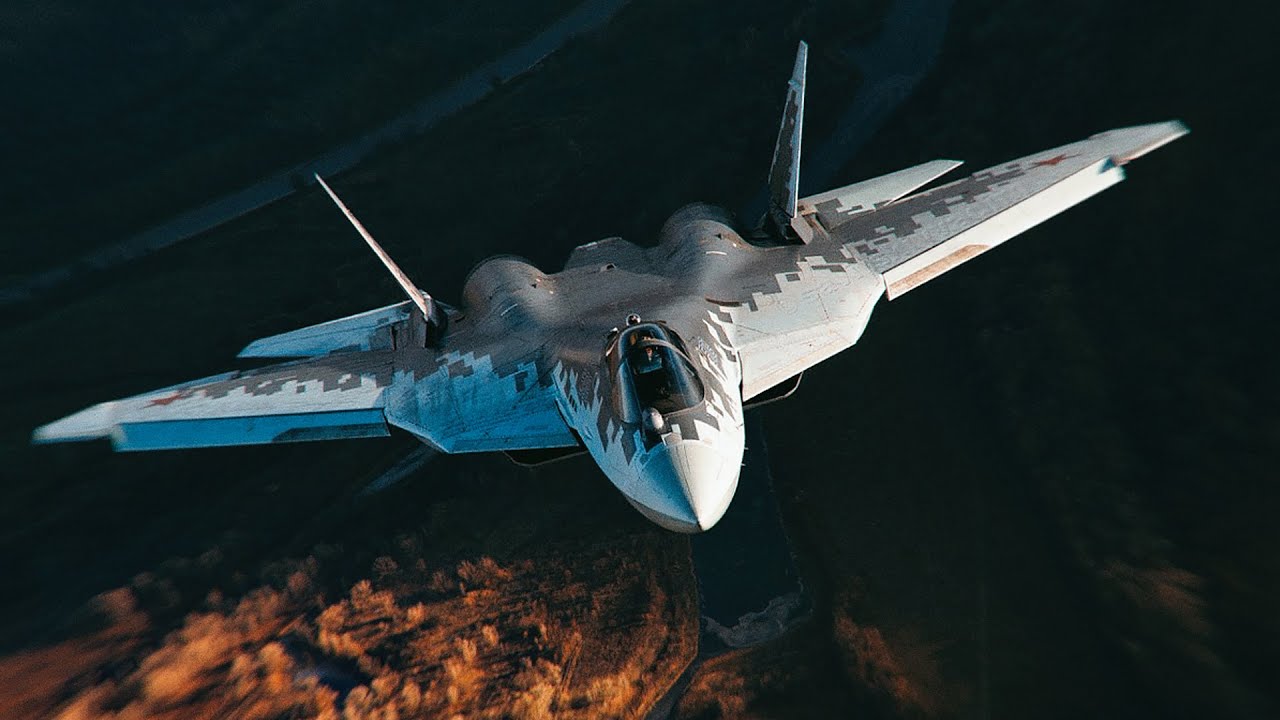
Best Russian Aircraft Fighter - It is a product of PAK FA (Russian: ПАК ФА, short for: Перспективный авиационный комплекс фронтовой авиации, Romanian: Perspektivenyy Aviatsioniii-complexed-front-cheap-frontive Miko-program 4 and more modern alternatives. /1). in 1999. Sukhoi's internal name for this aircraft is the T-50.
A multi-role fighter capable of air combat as well as ground and sea attacks, the Su-57 features stealth, super maneuverability, super cruise, integrated avionics and large internal payload capacity.
Best Russian Aircraft Fighter
The aircraft is expected to replace the MiG-29 and Su-27 in Russian military service and has also been marketed for export. The first prototype aircraft flew in 2010, but the program suffered a lengthy development due to various structural and technical problems that arose during testing, including the destruction of the first production aircraft in an accident prior to its delivery. After repeated delays, the first Su-57 served in the Russian Air Force (VKS).
Su 57: Why Russia Won't Send Its New Stealth Fighter To Ukraine
In 1979, the Soviet Union underlined the need for a next-generation fighter jet to become operational in the 1990s. This program became the I-90 (Russian: И-90, abbreviated: Истребитель 1990–х годов, lit. 'Fighter of the 1990s') and required the fighter to be sufficiently "multi-functional" (i.e. multi-role) Become a field. strike capability, and will eventually replace the MiG-29 and Su-27 in frontline tactical air service. Two further projects were developed to meet this need: MFI (Russian: МФИ, short for: Многофункциональный фронтовой истребитель, lit. 'Multifunctional Frontline Fighter'), abbreviated as LFI (Litian Litus), short: ЛФИ (Lits )'), conceptually work began in 1983.
Although not a participant in the MFI, Sukhoi began its own program in 1983 to develop technology for the next generation of fighter aircraft, resulting in the next-wing S-32 experimental aircraft, later the S-37 and redesigned Su-47. Given due to a lack of funds after the collapse of the Soviet Union, MFI was repeatedly delayed and the first flight of the MiG 1.44/1.42 prototype was not made until 2000, nine years behind schedule.
Due to high costs, MFI and LFI were canceled while the Russian Defense Ministry started work on a new generation fighter program; In 1999, the ministry launched the PAK FA or I-21 program, the competition being announced in April 2001.
Due to Russia's financial difficulties, the program aims to reduce costs by developing a single multi-role fifth-generation fighter that will replace the Su-27 and MiG-29. Further cost-saving measures include an intded size between the Su-27 and MiG-29 and a normal take-off weight of 28.6 tonnes (63,000 lb) for the MiG MFI and 26.8 tonnes (59,59,000 pounds) much more small . 000 pounds).
Russia Unveils New Stealth Fighter Jet To Compete With F 35
Sukhoi's approach to the PAK FA competition is fundamentally different from Makayan's; While Mikoyan proposed the three design bureaus (Mikoyan, Sukhoi, and Yakovlev) to work as a consortium with the team leading the design effort, Sukhoi proposed himself as lead designer from the outset, and entered into a collective bargaining agreement. The tire development and production cycle, from the propulsion and avionics supplier to the research facility. Additionally, the two companies have different design philosophies for the aircraft. The E-721 Mikoyan is smaller and more affordable, with a typical take-off displacement of 16–17 tons (35,000–37,000 lb) and a pair of Klimov VK-10M engines with 10–11 tons (98.1–108 N). with .22,000-24,300 lbf) of thrust each. In contrast, the Sukhoi T-50 will be relatively larger and more capable, with a modest target take-off weight of 22–23 tons (49,000–51,000 lb) and a pair of Levalka-Saturn AL-41F1 engines. Maximum thrust in class 14.5 tons (142 kN, 32,000 lbf).
In April 2002, the Ministry of Defense selected Sukhoi over Mikoyan as the winner of the PAK FA competition and headed the design bureau for the new aircraft.
Despite the merits of the proposal, Sukhoi's experience in the 1990s with the successful development of multiple variants of the Su-27 and many exports confirmed its financial feasibility.

Mikoyan continued to develop his E-721 as LMFS (Russian: ЛМФС, abbreviated: Лёгкий многофункциональный фронтовой файон, lit. 'Light Multifunctional Frontline Aircraft').
Russia Could Turn The Su 57 Into A Sixth Generation Fighter
PAK FA's research and development program is called Stolitsa (Russian: Столица, lit. 'Capital'). In 2002, Alexander Davidko was selected as chief designer of the T-50 at Sukhoi.
The Novosibirsk Aircraft Production Association (NAPO) and the Komsomolsk-on-Amur Aircraft Production Association (KnAAZ) will develop the new multi-role fighter, with KnAAZ carrying out final assembly in Komsomolsk-on-Amur.
Participated in the competition held in 2003, Scientific and Production Center of the Technocomplex, Ramskoye Instrument Building Design Bureau, Tikhomirov Instrument Design Research Institute (NIIP), Ural Optical and Mechanical Plant (UOMZ) in Yekaterinburg, Polet Company in Nizhny Novgorod. And the Central Scientific Research Radio Engineering Institute in Moscow was selected to develop the PAK FA avionics suite. In April 2004, NPO Lyulka-Saturn (now NPO Saturn) signed on with the development appointment of izdeliye 117 as contractor for the AL-41F1 gene.
Sukhoi uses the existing airframe as a testbed for various subsystems and concepts; The Su-47 tested the internal weapons bay, and the Su-27M prototype served as a testbed for the gene and flight control systems.
Syria, Airpower, And The Future Of Great Power War
In order to reduce development risks and spread associated costs, as well as to bridge the gap with existing fourth-generation fighters, Sukhoi applied some of the T-50's technologies and features, such as propulsion and some avionics, to the advanced derivatives of the Su-2. The 27 is called the T-10BM (Russian: БМ, for short: Большая моднаризника, lit. 'Major Modernization'), which was eventually purchased by the Russian Ministry of Defense in 2009 and entered service as the Su-35S.
In December 2004, the conceptual design and layout of the T-50 were finalized and approved by the Ministry of Defence; Government funding for the program began in 2005 and increased significantly in 2006, with detailed design underway.
On 8 August 2007, Commander-in-Chief of the Russian Air Force Alexander Zelen was quoted by Russian news agencies as saying that the development phase of the program had been completed and construction would begin on the first aircraft for flight tests, a three flight-capable T-With 50 prototypes. Designed in 2009.
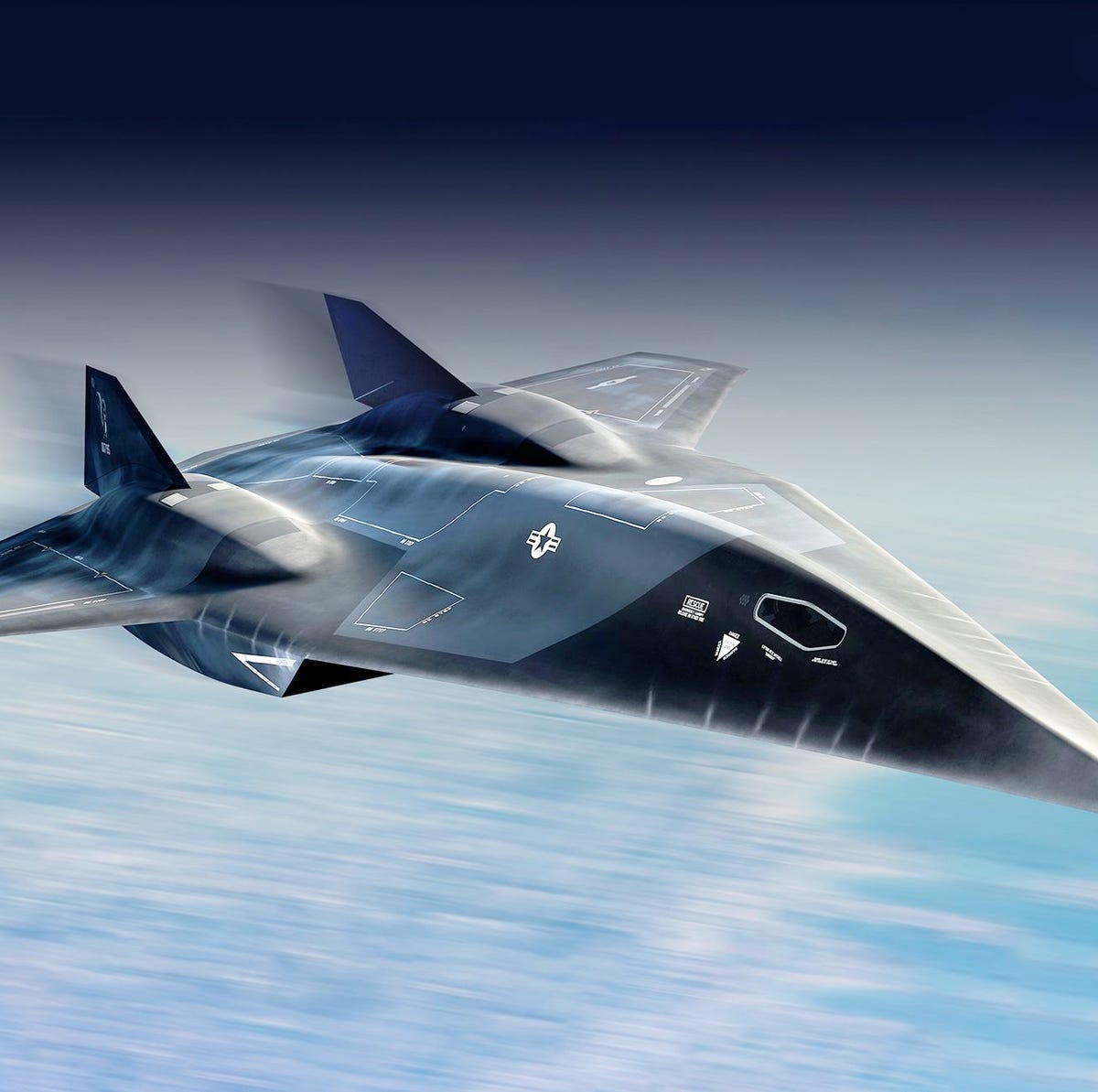

From the early stages of the PAK FA program, Russia sought foreign partnerships in the project to increase funding for its development and secure large export orders.
Why Is Poland Giving Mig 29 Fighter Jets To The Us
On 18 October 2007, Russia and India signed an agreement for Sukhoi and Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) to jointly develop a variant of the PAK FA called FGFA.
In September 2010, India and Russia agreed on a preliminary design agreement in which each country would invest $6 billion. A memorandum of understanding for the initial design was signed in December 2010, and development of the FGFA is expected to take 8-10 years.
However, in 2014, the Indian Air Force began to express concerns over performance, cost and maintenance. India finally left the partnership in 2018.
Operational flights of the T-50 have been repeatedly delayed since early 2007 after experiencing unspecified technical problems. In August 2009, Alexander Zelen admitted that the problems of genetic and technical research had not been resolved.
Russia Unveils Stealth Fighter Jet To Compete With F 35s
On 28 February 2009, Sukhoi General Director Mikhail Pogosyan announced that the airframe was nearly finished and the first prototype would be ready in August 2009.
On 20 August 2009, Pogosan said the first flight would be in July 2009. Konstantin Makiyko, deputy head of the Moscow-based Center for Analysis of Strategy and Technology, said that "chronologically speaking", the aircraft would likely make its first flight in January or February, adding that commercial production will take five to three years. .
Further flight testing was suspended when Deputy Prime Minister Sergei Ivanov announced in December 2009 that the first tests would begin in 2010.

The first taxi test was successfully completed on 24 December 2009, and the maiden flight of the first prototype aircraft, the T-50-1, took place on 29 January 2010.
Mig Russian At Fighter Jet Images, Stock Photos & Vectors
Piloted by Sukhoi test pilot Sergey Bogdan, the 47-minute maiden flight took place at Dzemgi KnAAPO Airport in Russia's Far East.
Prototype development will take place later than originally planned. As of October 2013, the test program has accumulated more than 450 flights in five aircraft.
A total of three flying and three non-flying T-50 prototypes will be produced for initial flight tests and country trials.
Initially, the program planned to produce up to six prototypes prior to the start of serial production; However, testing would reveal that early prototypes did not have sufficient fatigue life, with early structural cracks developing in the fuselage.
Top 12 Fighter Aircraft Of 1949
The aircraft then underwent a structural redesign, with changes including increased use of composite materials, a stronger fuselage to meet full life cycle requirements, a longer tail "stinger", and slightly larger wings; The sixth flyable prototype is the first of the newly developed "second stage" aircraft, with the initial five prototypes being considered "first stage" vehicles and requiring additional structural strength to continue flight testing.
The last two flying prototypes were production test articles of the Su-57 aircraft with full mission systems onboard.
While the "second stage" structure reduces the weight gain of the required force

Part 103 aircraft plans, part 103 aircraft, part 103 ultralight, part 103 ultralight kits, far part 103 ultralight aircraft, 103 ultralight aircraft for sale, part 103 ultralight for sale, part 103 ultralight aircraft kits, 103 ultralight aircraft, aerolite 103 ultralight aircraft, part 103 ultralight aircraft, part 103 ultralight aircraft for sale
0 Comments